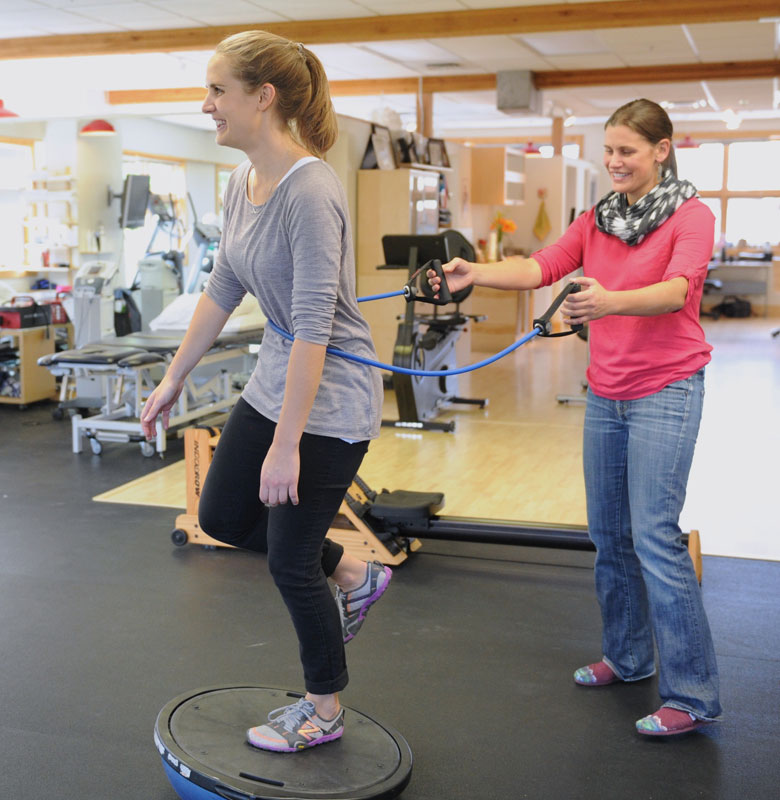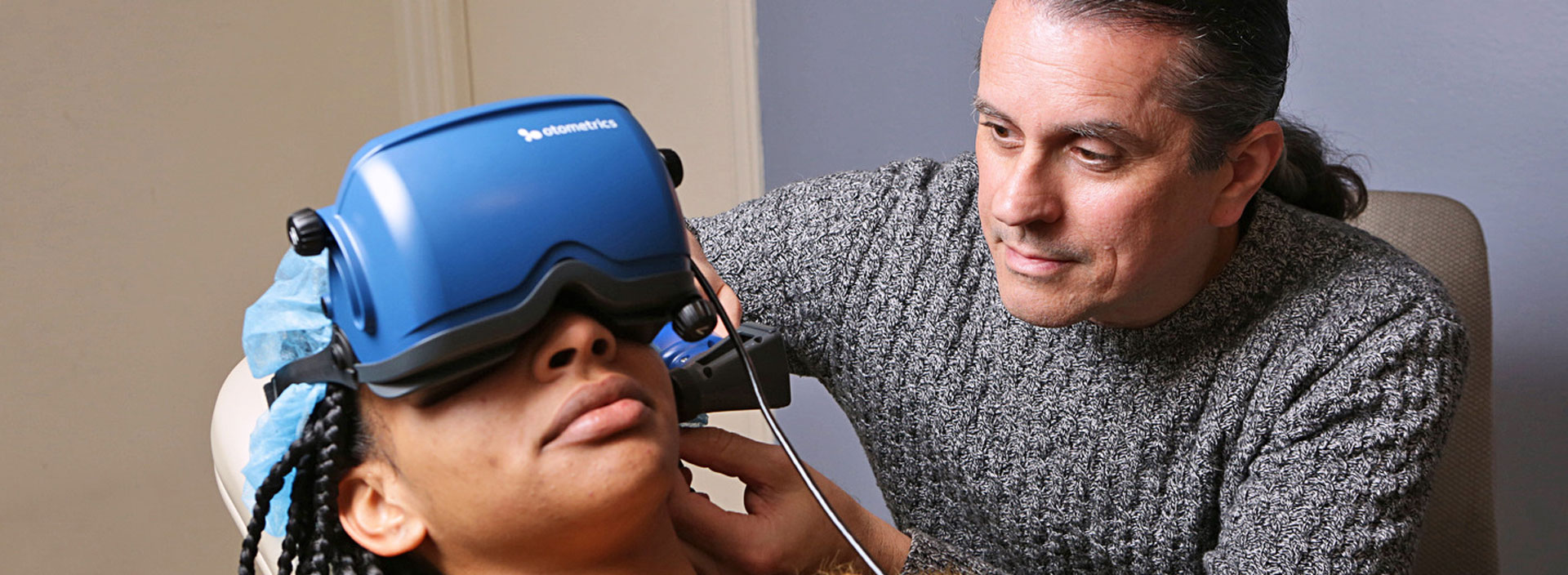
Vestibular Physiotherapy Recovery (VPR), or Vestibular Restoration Treatment (VRT) is a particular type of treatment proposed to mitigate both the essential and optional issues brought about by vestibular clutters. It is an activity-based program essentially designed to lessen dizziness, vertigo and gaze instability, or potentially imbalance and falls.
For a great many people with a vestibular disorder, the shortfall is long lasting and the fact that the measure of rebuilding of vestibular capacity is very small. Be that as it may, after vestibular system damage, individuals can feel better and function can return through remuneration. This happens on the grounds that our brain learns out how to utilize other senses.